Choosing the right vitamins for children requires careful consideration of their unique nutritional needs, safety requirements, and the quality of ingredients. Organic vitamins offer an appealing option for parents seeking natural, pesticide-free nutrition support for their growing children. Understanding what makes vitamins truly organic, which nutrients children need most, and how to select high-quality products helps ensure your child receives safe and effective nutritional support.

Understanding Organic Standards for Children's Vitamins
Organic vitamins must meet strict certification standards that prohibit synthetic pesticides, herbicides, artificial fertilizers, and genetically modified organisms in their production. For children's vitamins, this means the vitamin sources, whether from fruits, vegetables, or other natural materials, must be grown and processed according to organic agricultural standards.
The USDA Organic certification is the gold standard in the United States, requiring that at least 95% of ingredients be certified organic. Products labeled "100% Organic" contain only organic ingredients, while those labeled "Made with Organic" contain at least 70% organic ingredients. For children's vitamins, look for the USDA Organic seal to ensure the highest standards.
Organic certification also extends to processing methods, requiring that no synthetic additives, artificial colors, flavors, or preservatives be used. This is particularly important for children's vitamins, as kids can be more sensitive to artificial additives and may consume vitamins regularly over extended periods.
Third-party organic certifiers conduct regular inspections and testing to verify compliance with organic standards. Reputable children's vitamin manufacturers will clearly display their organic certification and certifying body information on their packaging and websites.

Essential Nutrients for Growing Children
Children have unique nutritional needs that differ significantly from adults due to their rapid growth, developing immune systems, and high activity levels. Understanding these needs helps parents prioritize which nutrients are most important when selecting organic vitamins.
Vitamin D is crucial for bone development, immune function, and overall growth. Many children, especially those with limited sun exposure or living in northern climates, don't get adequate vitamin D from sunlight and food sources alone. The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends 400-600 IU daily for most children, though individual needs may vary.
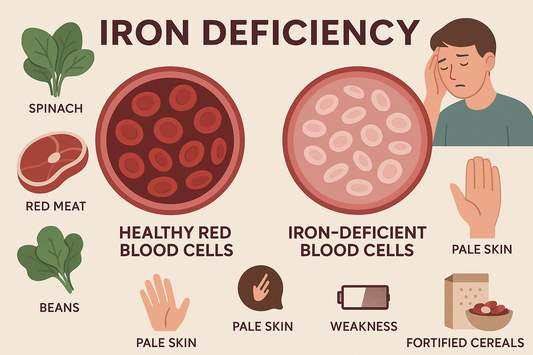
Iron supports healthy blood formation and cognitive development, with deficiency being relatively common in children, particularly toddlers and adolescent girls. However, iron can be dangerous in excess, so iron-containing vitamins should only be used when specifically recommended by a healthcare provider after appropriate testing.
Vitamin B12 is essential for nervous system development and energy metabolism. Children following vegetarian or vegan diets are at particular risk for B12 deficiency, making supplementation especially important for these families choosing plant-based lifestyles.
Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly DHA, support brain development and cognitive function. While not always included in traditional multivitamins, organic sources of omega-3s from algae or fish oil specifically designed for children can be valuable additions to a child's nutrition regimen.
Vitamin C supports immune function and helps with iron absorption. While severe deficiency is rare in developed countries, many children don't consume adequate fruits and vegetables to optimize their vitamin C intake, making organic supplementation beneficial.

Age-Specific Nutritional Considerations
Children's nutritional needs change significantly as they grow, requiring different approaches to vitamin supplementation at various developmental stages.
Infants under 12 months have very specific nutritional needs that are typically met through breast milk or formula. The only vitamin commonly recommended for infants is vitamin D, usually given as liquid drops. Organic options are available, though the organic status is less critical for single-nutrient supplements compared to complex multivitamins.
Toddlers aged 1-3 years are transitioning to solid foods and may have erratic eating patterns, making them good candidates for comprehensive organic multivitamins. This age group often benefits from chewable or liquid formulations that are easier to administer and more appealing to young children.
Preschoolers aged 4-6 years are developing food preferences and may go through phases of selective eating. Organic gummy vitamins often appeal to this age group, though parents should be mindful of sugar content and ensure the gummies don't become confused with candy.
School-age children aged 7-12 years have increased nutritional needs due to growth spurts and higher activity levels. This group can typically handle tablet or capsule forms of vitamins and may benefit from more comprehensive formulations that include minerals alongside vitamins.
Adolescents have the highest nutritional needs of any age group due to rapid growth, hormonal changes, and often irregular eating patterns. Teenagers may require adult-level dosing of certain nutrients and often benefit from targeted supplementation based on their individual dietary patterns and lifestyle factors.

Forms and Delivery Methods for Children
The form and delivery method of children's vitamins significantly affects both compliance and absorption, making it important to choose options that work well for your child's age and preferences.
Liquid vitamins offer excellent absorption and are ideal for infants, toddlers, and children who have difficulty swallowing pills. Organic liquid vitamins often use natural fruit concentrates for flavoring and avoid artificial colors and preservatives. However, liquid vitamins may have shorter shelf lives and require refrigeration.
Chewable tablets provide a good compromise between ease of administration and stability. Organic chewable vitamins often use natural fruit flavors and colors derived from organic sources like beets or turmeric. The chewing action can actually aid in the initial breakdown and absorption of nutrients.
Gummy vitamins are often the most appealing to children but present some challenges. The gummy format limits which nutrients can be included and at what levels, as some vitamins are not stable in gummy form. Organic gummy vitamins use organic sugar or natural sweeteners but still contain sugars that can contribute to dental issues if oral hygiene isn't maintained.
Powder formulations can be mixed into food or drinks, making them ideal for children who refuse to take vitamins directly. Organic vitamin powders often have neutral flavors that don't significantly alter the taste of foods, making them easier to incorporate into daily routines.
Capsules that can be opened and sprinkled on food offer flexibility for children who can't swallow pills but need higher doses or specific formulations not available in chewable forms. This method works well for older children who are transitioning to adult-style supplements.

Quality Indicators and Safety Considerations
Selecting high-quality organic vitamins for children requires understanding key quality indicators and safety considerations that go beyond organic certification.
Third-party testing for purity and potency ensures that vitamins contain what's listed on the label and are free from contaminants. Look for products that have been tested by independent laboratories and provide certificates of analysis or quality assurance information.
Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) certification indicates that the manufacturer follows strict quality control procedures during production. This is particularly important for children's vitamins, as quality control issues can have serious consequences for developing bodies.
Age-appropriate dosing is crucial for children's vitamins, as adult formulations can provide excessive amounts of certain nutrients that may be harmful to children. Reputable manufacturers will clearly indicate appropriate age ranges and dosing instructions for their products.
Allergen information should be clearly labeled, particularly for common allergens like soy, dairy, nuts, and gluten. Many organic children's vitamins are formulated to be free from major allergens, but it's important to verify this information if your child has known sensitivities.
Expiration dates and proper storage instructions help ensure the vitamins maintain their potency and safety. Organic vitamins may have shorter shelf lives than conventional vitamins due to the absence of synthetic preservatives, making proper storage and attention to expiration dates even more important.

Common Nutrient Gaps in Children's Diets
Understanding common nutritional gaps in children's diets helps parents prioritize which nutrients to focus on when selecting organic vitamin supplements.
Fiber intake is often inadequate in children's diets, though this is typically addressed through food rather than supplements. However, some organic children's supplements include prebiotic fibers that support digestive health and nutrient absorption.
Calcium intake may be insufficient in children who don't consume adequate dairy products or calcium-rich plant foods. Organic calcium supplements for children often use calcium citrate or calcium carbonate derived from organic sources and may include vitamin D and magnesium for optimal absorption and utilization.
Magnesium deficiency is increasingly common in children's diets due to processed food consumption and reduced intake of magnesium-rich whole foods. Organic magnesium supplements for children often use gentle forms like magnesium glycinate that are well-absorbed and less likely to cause digestive upset.
Zinc supports immune function and growth, and mild deficiencies are not uncommon in children, particularly those with limited meat intake. Organic zinc supplements for children typically use chelated forms that are better absorbed and less likely to cause stomach upset.
Vitamin A intake may be inadequate in children who don't consume enough orange and dark green vegetables. Organic vitamin A supplements often use natural beta-carotene from organic sources rather than synthetic vitamin A, which is safer for children as beta-carotene converts to vitamin A as needed.

Addressing Picky Eating Through Supplementation
Many parents turn to vitamins to address nutritional concerns related to picky eating, though supplements should complement rather than replace efforts to improve dietary variety.
Short-term supplementation can provide peace of mind and nutritional insurance while working on expanding a child's diet. Organic multivitamins can help fill gaps during particularly challenging phases of picky eating, ensuring children receive essential nutrients even when food intake is limited.
Comprehensive formulations may be beneficial for children with very restricted diets, providing a broad spectrum of nutrients that might be missing from their food intake. However, it's important to continue encouraging dietary variety rather than relying solely on supplementation.
Taste and texture considerations are crucial for picky eaters, who may also be sensitive to the taste or texture of vitamins. Organic vitamins often have more natural, milder flavors that may be better accepted by sensitive children.
Gradual introduction of vitamins can help picky eaters accept supplementation. Starting with small doses or mixing powdered vitamins into preferred foods can help children gradually accept vitamin supplementation.
Working with healthcare providers helps ensure that supplementation appropriately addresses specific nutritional concerns related to picky eating while maintaining focus on long-term dietary improvement.
Special Dietary Considerations
Children following special diets may have unique nutritional needs that require targeted organic vitamin supplementation.
Vegetarian and vegan children need particular attention to vitamin B12, iron, zinc, and omega-3 fatty acids. Organic supplements designed for plant-based diets often provide these nutrients in forms that are well-absorbed and appropriate for children's developing systems.
Children with food allergies may have limited dietary options that affect their nutritional intake. Organic, allergen-free vitamin formulations can help ensure these children receive adequate nutrition while avoiding problematic ingredients.
Children with digestive issues like celiac disease or inflammatory bowel conditions may have impaired nutrient absorption, requiring higher-quality, more bioavailable vitamin formulations. Organic vitamins often use more gentle, easily absorbed forms of nutrients that may be better tolerated.
Children following elimination diets for various health reasons may benefit from comprehensive organic vitamin supplementation to prevent nutritional deficiencies during dietary restriction periods.
Reading Labels and Understanding Ingredients
Understanding how to read and interpret children's vitamin labels helps parents make informed choices about organic products.
Ingredient lists should be short and recognizable, particularly for organic products. Avoid products with long lists of artificial additives, colors, or preservatives, even if the product claims to be organic.
Dosage information should be clearly stated and age-appropriate. Be wary of products that don't provide clear dosing instructions or that seem to provide adult-level doses for children.
Organic certification seals should be prominently displayed and clearly indicate which certifying body has approved the product. Different countries have different organic standards, so understanding the certification system helps ensure quality.
Nutritional facts panels should clearly indicate the amount of each nutrient per serving and the percentage of daily value where established for children. Keep in mind that daily values are often based on adult needs, so percentages may seem high for children's products.

Potential Risks and Precautions
While organic vitamins are generally safer than conventional alternatives, there are still important safety considerations for children's supplementation.
Overdose risks exist with any vitamin supplementation, particularly with fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K) that can accumulate in the body. Even organic vitamins can cause toxicity if taken in excessive amounts, making proper dosing crucial.
Iron poisoning is a particular concern with children's vitamins, as iron can be fatal in overdose. Keep all iron-containing vitamins out of reach of children and follow dosing instructions carefully. Many children's multivitamins are formulated without iron for this reason.
Interaction with medications can occur even with organic, natural vitamins. Some vitamins can affect the absorption or effectiveness of prescription medications, making it important to discuss supplementation with healthcare providers.
Quality variations can exist even among organic products, as organic certification doesn't guarantee potency or bioavailability. Choose reputable manufacturers with good quality control practices and third-party testing.
Cost Considerations and Value Assessment
Organic children's vitamins typically cost more than conventional alternatives, making it important to assess value and make informed purchasing decisions.
Price per serving varies significantly among organic children's vitamins, and higher prices don't always indicate better quality. Compare products based on the amount and quality of nutrients provided per serving rather than just the overall bottle price.
Bulk purchasing or subscription services may offer cost savings for families committed to long-term vitamin supplementation. However, consider shelf life and storage requirements when buying larger quantities.
Generic versus brand name organic vitamins may offer similar quality at different price points. Some store brands use the same manufacturers as premium brands but at lower prices due to different marketing and packaging approaches.
Insurance coverage for vitamins is rare, but some flexible spending accounts or health savings accounts may cover vitamin supplements when prescribed by healthcare providers for specific deficiencies.
Implementation and Compliance Strategies
Successfully incorporating organic vitamins into children's routines requires thoughtful implementation strategies that promote compliance and effectiveness.
Establishing consistent routines helps children remember to take vitamins and makes supplementation a normal part of their day. Many families find success taking vitamins with breakfast or another consistent daily activity.
Making vitamins appealing through positive associations, special vitamin containers, or reward systems can improve compliance, particularly with younger children. However, avoid making vitamins seem like candy or treats to prevent overconsumption.
Age-appropriate education about why vitamins are important can help older children understand the value of supplementation and take more responsibility for their vitamin routine.
Monitoring and adjusting approaches based on your child's response, preferences, and changing needs ensures that vitamin supplementation remains effective and appropriate over time.
Organic vitamins can provide valuable nutritional support for children when selected carefully and used appropriately. The key is choosing high-quality products that meet your child's specific needs while maintaining realistic expectations about what supplementation can and cannot accomplish. Remember that vitamins work best as part of a comprehensive approach to children's health that includes a varied diet, regular physical activity, adequate sleep, and appropriate medical care. By focusing on quality, safety, and individual needs, parents can effectively use organic vitamins to support their children's optimal growth and development.