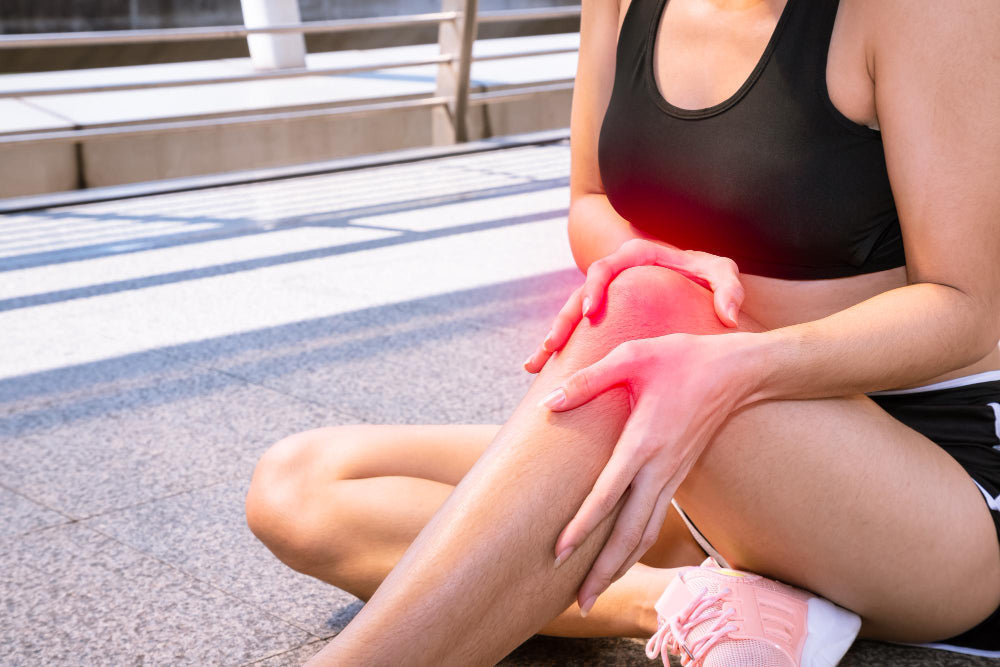
Introduction to Muscle Cramps
Muscle cramps, including leg cramps, are sudden and involuntary contractions of leg muscles that can cause severe pain and discomfort. Leg cramps can happen suddenly and unpredictably, often while sleeping or at rest.
Leg cramps are a common and often painful condition that can affect various areas of the lower body, including the calves, feet, thighs, and toes. These cramps result from the involuntary tightening of muscles, which can range from mild discomfort to severe, painful contractions. In some cases, the pain can be intense enough to wake individuals from sleep, significantly disrupting their rest.
The Importance of Understanding Leg Cramps
Understanding leg cramps is key to managing and preventing them effectively. While many episodes are harmless and temporary, recurring cramps can sometimes indicate an underlying health issue. For instance, conditions such as liver disease or high blood pressure may present leg cramps as a symptom, emphasizing the importance of consulting a healthcare provider if cramps are frequent or severe.
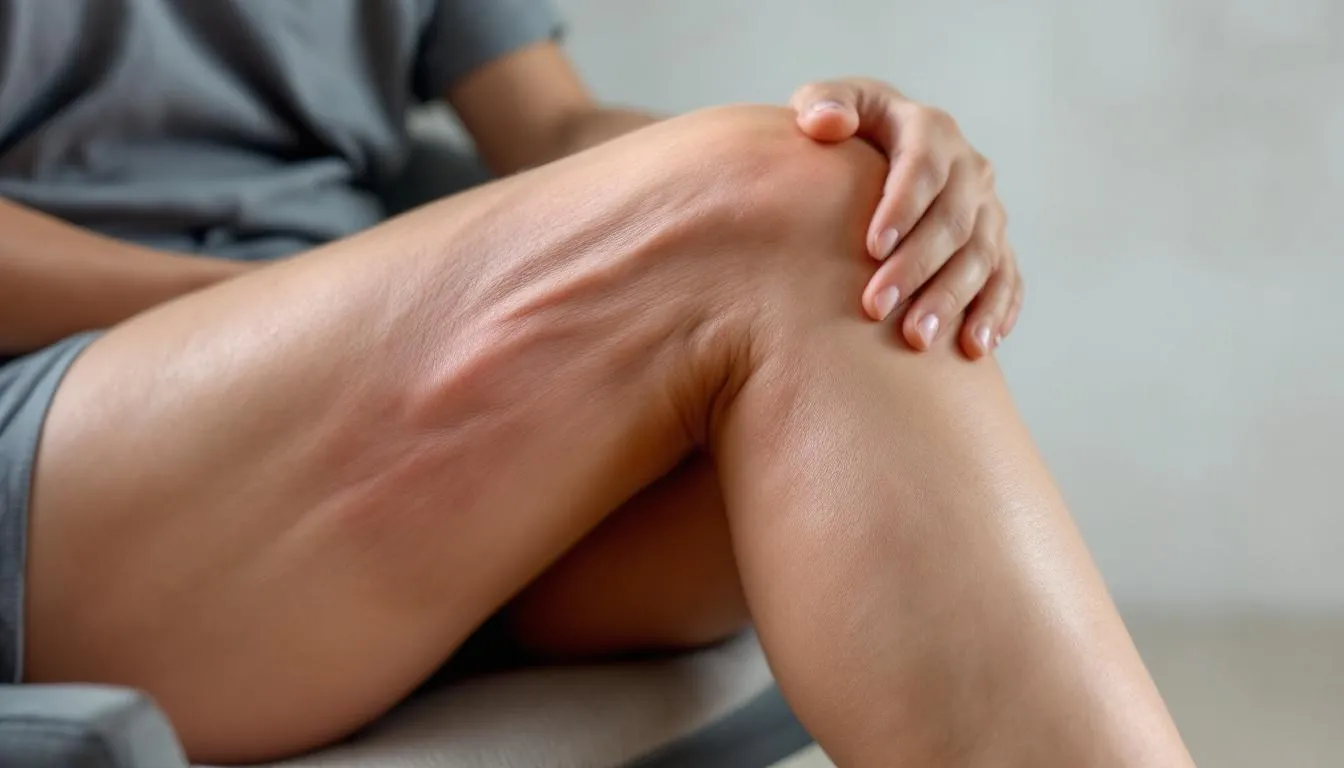
Understanding the Condition
- Leg cramps affect the leg muscles, causing sudden pain and muscle fatigue. Dehydration and electrolyte imbalances, such as low potassium or magnesium, can lead to leg cramps.
- Nocturnal leg cramps occur at night, disrupting sleep and causing discomfort.
- Muscle cramps can be caused by muscle weakness, poor blood flow, or underlying medical conditions.
- Leg cramps can be a side effect of certain medications or a symptom of an underlying condition.
- Preventing leg cramps requires a comprehensive approach, including exercises, stretches, and lifestyle modifications. While these strategies can reduce the frequency, cramps may still end up happening occasionally.
Symptoms and Duration
- Leg cramps cause sudden pain, muscle tightness, and discomfort in the affected leg muscle.
- Cramps can last from a few seconds to several minutes, with some episodes lasting up to 10 minutes.
- Symptoms can include muscle weakness, numbness, swelling, and skin changes.
- Leg cramps can be severe, causing significant discomfort and disrupting daily activities.
- Most cramps resolve on their own, but some may require medical attention.
Risk Factors
- Risk factors for leg cramps include pregnancy, age, and certain medical conditions, such as high blood pressure or liver disease.
- Muscle fatigue, dehydration, and electrolyte imbalances can contribute to leg cramps.
- Playing sports, exercising, or engaging in strenuous activities can increase the risk of leg cramps.
- A charley horse is a common term for a leg cramp, especially in the calf muscle.
- Leg cramps can be a symptom of an underlying condition, such as a blood flow disorder or nerve damage, and certain treatments may carry risks and side effects that should be discussed with a healthcare provider.
Medical Conditions
Medications That May Cause Cramps
Certain medications can trigger muscle cramps, including leg cramps, as an unexpected side effect. These medicines may interfere with the normal function of muscles and nerves, sometimes leading to sudden pain, muscle fatigue, or even muscle weakness. If you notice leg cramps after starting a new prescribed medication, it’s important to discuss your symptoms with your doctor or pharmacist, as an alternative treatment may be available.

Preventing Leg Cramps: A Holistic Approach
Leg cramps can be uncomfortable and disruptive, but the good news is that they are often preventable with the right strategies. Prevention focuses on maintaining healthy habits, such as staying active, staying hydrated, and making small but impactful lifestyle changes. By taking proactive steps to care for your muscles and body, you can significantly reduce the risk of painful cramping episodes. Here are some practical tips to help you prevent leg cramps:
Preventing Leg Cramps
Preventing leg cramps requires a comprehensive approach, including regular exercises, stretches, and lifestyle modifications.
Calf muscles are prone to cramps, and stretching can help prevent episodes.
Drink plenty of fluids, such as water or electrolyte-rich beverages, maintaining a balanced diet, and avoiding dehydration can help prevent leg cramps.
Keeping blankets loose, avoiding constrictive clothing, and maintaining good posture can reduce the risk of leg cramps.
Gentle stretching, massaging, and heat application can help relax the muscles, prevent cramping, and relieve leg cramps.
Treatment Options
Treatment options for leg cramps include gentle stretching, heat application (such as using a heating pad), and medication.
Muscle relaxants, such as quinine, can be prescribed for severe or frequent leg cramps.
Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, can help alleviate pain and discomfort.
Alternative therapies, such as massage or acupuncture, can help treat and manage leg cramps.
In severe cases, medical attention may be necessary to treat underlying conditions causing leg cramps.
Stretches for Relief
Stretches can help relieve and prevent leg cramps, especially in the calf muscles.
Gently stretching, such as toe curls or ankle rotations, can help loosen tight muscles.
Stretching the feet and toes can also help relieve cramps.
Standing or leaning forward can help stretch the calf muscles and relieve cramps.
Regular exercises, such as walking or jogging, can help improve circulation and reduce the risk of leg cramps.
Stretching before bed can help prevent nocturnal leg cramps.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Medical attention is necessary if leg cramps are severe, frequent, or persistent.
Underlying conditions, such as liver disease or kidney disease, require prompt medical attention.
If leg cramps are accompanied by other symptoms, such as numbness, weakness, or skin changes, medical attention is necessary.
A healthcare professional can help diagnose and manage underlying conditions contributing to leg cramps.
Medical attention is necessary if leg cramps are causing significant discomfort or disrupting daily activities.
Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle modifications, such as regular exercise, a balanced diet, and stress management, can help prevent and manage leg cramps.
Maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding smoking, and limiting alcohol consumption can reduce the risk of leg cramps.
Getting enough sleep, practicing good sleep hygiene, and avoiding strenuous activities before bed can help prevent nocturnal leg cramps.
Managing stress through relaxation techniques, such as meditation or deep breathing, can help reduce the risk of leg cramps.
Staying hydrated, avoiding dehydration, and maintaining electrolyte balance can help prevent leg cramps.
Managing Episodes
Managing leg cramp episodes requires a comprehensive approach, including gentle stretching, heat application, and medication.
Keeping a cramp diary can help identify triggers and patterns.
Avoiding triggers, such as certain foods or activities, can help prevent leg cramps.
Practicing self-care, such as massage or relaxation techniques, can help manage stress and reduce the risk of leg cramps.
Seeking medical attention if leg cramps are severe or persistent is crucial for effective management.
Conclusion
Leg cramps are a common condition that can be managed and prevented with a comprehensive approach.
Understanding the condition, identifying risk factors, and implementing lifestyle modifications can help reduce the risk of leg cramps.
Gentle stretching, heat application, and medication can help relieve and prevent leg cramps.
Medical attention is necessary if leg cramps are severe, frequent, or persistent, or if underlying conditions are suspected.
By taking a proactive approach to managing leg cramps, individuals can reduce discomfort, improve quality of life, and prevent complications.













