Optimal Dosage for D Mannose: A Guide to UTI Prevention and Relief
Introduction to Urinary Tract Infections
Urinary tract infections represent one of the most prevalent bacterial infections affecting millions of individuals worldwide, with women experiencing disproportionately higher rates due to anatomical factors including a shorter urethra that facilitates bacterial migration from the perineal area to the urinary system. The incidence of UTIs increases significantly with age, sexual activity, pregnancy, and various medical conditions that compromise immune function or urinary tract integrity.
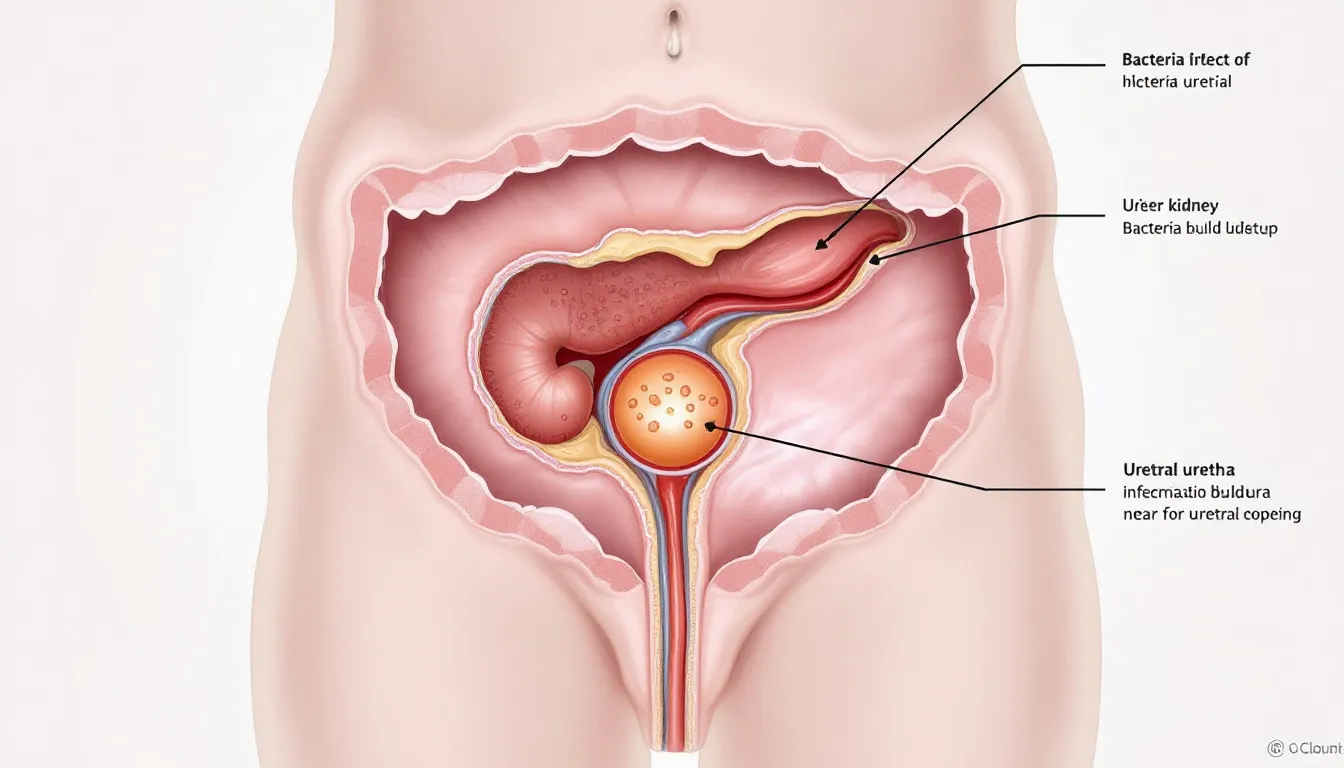
The pathophysiology of UTIs typically involves the ascension of pathogenic bacteria through the urethra into the bladder, where they establish colonization and trigger inflammatory responses. Bacteria enter the urinary tract primarily through the urethra, initiating infection by adhering to the lining of the urinary tract. Escherichia coli accounts for approximately 80-85% of uncomplicated UTIs, though other organisms including Klebsiella, Enterococcus, and Staphylococcus saprophyticus can also cause urinary tract infections under specific circumstances.
Clinical manifestations of UTIs encompass a constellation of symptoms including dysuria (burning sensation during urination), urinary frequency and urgency, suprapubic discomfort, and alterations in urine characteristics such as cloudiness, strong odor, or hematuria. Lower urinary tract infections, clinically referred to as acute cystitis, typically present with localized bladder symptoms, while upper tract involvement may progress to systemic symptoms including fever, chills, and flank pain indicating pyelonephritis.
The significance of prompt recognition and appropriate treatment of UTIs cannot be overstated, as untreated infections can progress to serious complications including ascending pyelonephritis, urosepsis, and potential kidney damage. Recurrent UTIs, defined as two or more infections within six months or three or more within twelve months, pose particular challenges and may require specialized management approaches including prophylactic interventions and lifestyle modifications.

Understanding D-Mannose: Mechanism and Scientific Foundation
D-mannose represents a naturally occurring simple sugar that belongs to the aldohexose family and shares structural similarities with glucose, differing only in the configuration of hydroxyl groups at specific carbon positions. This monosaccharide occurs naturally in various fruits including cranberries, blueberries, and apples, as well as birch bark, though therapeutic concentrations typically require supplementation due to limited dietary availability and rapid metabolic clearance.
After ingestion, D-mannose is efficiently absorbed in the human body through the gastrointestinal tract, enters the bloodstream, and is largely excreted unchanged in the urine. Within the human body, D-mannose participates in glycosylation processes and supports immune function, but is not metabolized like typical sugars, making it suitable for urinary health support.
The therapeutic mechanism of D-mannose in UTI prevention centers on its ability to competitively inhibit bacterial adhesion to uroepithelial cells lining the urinary tract. E. coli bacteria utilize specific adhesins, particularly Type 1 fimbriae with mannose-sensitive binding properties, to attach to mannose-containing glycoproteins on the surface of urinary tract epithelium. When D-mannose is present in sufficient concentrations within the urinary system, it serves as a competitive substrate, binding to bacterial adhesins and preventing pathogen attachment to host tissue. D mannose makes a significant contribution to urinary tract health by preventing bacterial colonization without disrupting normal flora.
Research demonstrates that unbound bacteria in the presence of D-mannose are subsequently eliminated through normal urinary flow, effectively reducing bacterial load and preventing the establishment of infection. This anti-adhesive mechanism represents a novel approach to UTI prevention that differs fundamentally from antibiotic interventions, as it does not directly kill bacteria but rather prevents their colonization of urinary tract surfaces.
Clinical studies investigating D-mannose efficacy have demonstrated promising results in both UTI prevention and symptom management. These studies evaluated specific D-mannose dosage protocols, often adjusting the amount based on infection severity and individual factors. A randomized controlled trial published in the World Journal of Urology found that D-mannose was as effective as trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole for preventing recurrent UTIs while producing fewer adverse effects. Additional research has shown that D-mannose can reduce UTI recurrence rates by up to 60% in susceptible populations when used as prophylactic therapy.
Benefits of D-Mannose
As someone who's spent decades caring for others, I'm always excited to share knowledge about gentle, natural approaches that can truly make a difference in people's lives. D-mannose, this wonderful simple sugar that nature provides us, has become one of my go-to recommendations for dear friends and family members who struggle with those frustrating urinary tract infections. What I find so beautiful about D-mannose is how it works with your body's own wisdom – it gently prevents E. coli and other troublesome bacteria from clinging to your bladder wall and urinary tract lining. Rather than fighting against your system, it simply interferes with that very first step where bacteria try to take hold, naturally reducing the chance of infection developing. This makes it such a valuable ally, whether you're looking to prevent UTIs or find relief when they occur.
Over the years, I've guided many people toward D-mannose tablets or powder as a wonderfully convenient and effective way to nurture their bladder health. What I love about these mannose tablets is their flexibility – you can use them on their own as part of your natural wellness routine, or work alongside your healthcare provider to combine them with antibiotics when needed. This gives you options and puts you in control of your health journey. Because D-mannose works by gently encouraging bacteria to let go of the bladder rather than destroying them outright, it honors your body's delicate balance. It won't disrupt those beneficial bacteria that keep you healthy, and it doesn't contribute to the concerning issue of antibiotic resistance that we see too often these days.
What brings me such peace of mind when recommending D-mannose is its remarkable gentleness and safety. In all my years of experience, I've seen how well most people tolerate this natural helper, with very few side effects to worry about. This makes it such a blessing for those dealing with recurring UTIs who need something they can rely on long-term. The fact that it comes straight from nature and works so gently with your urinary tract has made D-mannose products increasingly cherished by people seeking safe, non-antibiotic paths to wellness. Whether you choose to use it as a preventive measure in your daily routine or as part of a more comprehensive approach to managing UTIs, D-mannose offers you a simple, effective way to support your bladder health and reduce the burden these infections can place on your life.
Optimal Dosage Protocols for UTI Prevention
Establishing appropriate D-mannose dosing protocols requires consideration of multiple factors including the intended use (prevention versus treatment), individual patient characteristics, and the severity of UTI history. Current evidence suggests that prophylactic dosing differs significantly from therapeutic interventions, with prevention typically requiring lower, sustained daily doses while active infections may benefit from higher, more frequent administration.
For UTI prevention in individuals with recurrent UTI, research supports daily doses of 1-2 grams of D-mannose, typically administered as a single dose or divided into two smaller doses throughout the day. This prophylactic regimen has demonstrated efficacy in reducing UTI recurrence rates while maintaining an excellent safety profile with minimal reported adverse effects. For ongoing prevention, a maintenance dose is often recommended to help sustain bladder health and minimize the risk of future infections.
Timing of D-mannose administration can influence therapeutic efficacy, with some evidence suggesting that bedtime dosing may provide enhanced protection due to prolonged urinary contact time during overnight periods when urination frequency naturally decreases. Additionally, post-coital administration has shown particular benefit for women who experience UTIs related to sexual activity, with doses of 1-2 grams taken within two hours of intercourse providing protective effects.
The duration of prophylactic D-mannose therapy varies based on individual risk factors and UTI history, with some patients requiring long-term administration for sustained protection while others may benefit from shorter courses during high-risk periods. Clinical experience suggests that patients with frequent recurrent UTIs may require continuous prophylaxis for 3-6 months before attempting dose reduction or discontinuation.
Individual dose optimization should consider factors such as body weight, kidney function, concurrent medications, and previous response to therapy. While standard dosing protocols provide effective starting points, some patients may require dose adjustments based on clinical response and tolerance patterns observed during initial treatment periods.
Therapeutic Dosing for Active UTI Management
When utilized for managing active UTI symptoms, D-mannose dosing protocols typically involve higher doses administered more frequently for treating UTIs, aiming to achieve therapeutic urinary concentrations capable of disrupting established bacterial biofilms and preventing further bacterial adhesion. Current evidence supports dosing ranges of 1.5-3 grams administered 2-3 times daily during active infection periods.
The rationale for increased dosing during active infections stems from the need to overcome established bacterial colonization and achieve sufficient urinary concentrations to compete effectively with bacterial adhesins already bound to uroepithelial surfaces. Higher doses also compensate for increased bacterial loads present during active infections and the potential presence of biofilm formations that may protect bacteria from anti-adhesive interventions.
Treatment duration for active UTIs typically ranges from 3-7 days, depending on symptom severity and clinical response. Some patients may experience symptom improvement within 24-48 hours of initiating therapy, while others may require the full treatment course to achieve optimal results. Monitoring symptom progression and urinary characteristics can guide treatment duration decisions.
Combination therapy approaches that integrate D-mannose with conventional antibiotic treatments have shown promise in clinical practice, potentially enhancing bacterial clearance while reducing the risk of antibiotic resistance development. When used concurrently with antibiotics, D-mannose may help prevent bacterial reattachment following antibiotic-induced bacterial death, potentially reducing treatment failure rates.
The transition from therapeutic to prophylactic dosing should be gradual, with patients typically continuing higher doses for 2-3 days following symptom resolution before transitioning to a maintenance dose or maintenance prophylactic regimens. This approach helps ensure complete bacterial clearance while establishing protective urinary concentrations for ongoing prevention.

Special Populations and Dosing Considerations
Pediatric Populations
Children with recurrent UTIs present unique dosing challenges due to differences in pharmacokinetics, body weight considerations, and the need for age-appropriate formulations. Current pediatric dosing recommendations suggest weight-based calculations of approximately 15-25 mg/kg/day for prophylaxis, though limited pediatric-specific research necessitates careful clinical monitoring and potential dose adjustments.
Safety considerations in pediatric populations include ensuring appropriate formulations that minimize choking hazards and provide accurate dosing capabilities. Powder formulations may be preferred for younger children as they can be mixed with liquids and doses can be precisely measured based on individual weight requirements.
Pregnancy and Lactation
Pregnant women experience increased UTI susceptibility due to physiological changes affecting urinary tract function, making safe and effective prevention strategies particularly important. While D-mannose appears to have an excellent safety profile with minimal systemic absorption, limited specific safety data in pregnancy necessitates careful risk-benefit evaluation and consultation with healthcare providers.
Current evidence suggests that D-mannose does not cross the placental barrier in significant quantities due to its rapid renal elimination, potentially making it safer than many conventional UTI prevention strategies. However, pregnant women should initiate D-mannose therapy only under medical supervision with appropriate monitoring for both maternal and fetal well-being.
Patients with Diabetes
Individuals with diabetes require special consideration when using D-mannose due to potential effects on blood glucose monitoring and the theoretical possibility of glycemic interference. While D-mannose metabolism differs significantly from glucose and typically does not affect blood sugar levels, diabetic patients should monitor glucose more frequently when initiating therapy. Individuals with metabolic syndrome, which often co-occurs with diabetes, may also require individualized monitoring and dosing adjustments when using D-mannose.
Dosing adjustments may be necessary in diabetic patients with compromised kidney function, as reduced renal clearance could potentially affect D-mannose elimination and therapeutic efficacy. Regular monitoring of kidney function and glucose control can guide appropriate dose modifications in this population.
Patients with Kidney Disease
Individuals with chronic kidney disease present complex dosing challenges due to altered drug elimination and the potential for accumulation of renally cleared substances. While D-mannose is primarily eliminated unchanged through the kidneys, its safety profile in patients with significant renal impairment remains incompletely characterized.
Conservative dosing approaches starting with lower doses and careful clinical monitoring are recommended for patients with moderate to severe kidney disease. Patients with a history of kidney transplant should consult their healthcare provider before starting D-mannose therapy due to their unique medical needs. Consultation with nephrology specialists may be appropriate for patients with advanced chronic kidney disease considering D-mannose therapy.
Administration Guidelines and Practical Considerations
Formulation Selection
D-mannose is available in multiple formulations including capsules, tablets, and powder forms, each offering distinct advantages depending on patient preferences and clinical circumstances. Powder formulations provide the greatest dosing flexibility and may achieve faster dissolution and absorption, while capsule and tablet forms offer convenience and precise dosing for routine administration.
When selecting formulations, consider factors such as patient age, swallowing ability, taste preferences, and dosing accuracy requirements. Powder forms can be mixed with water, juice, or other beverages to improve palatability, though mixing with acidic beverages may enhance urinary acidification and potentially improve therapeutic efficacy.
Timing and Food Interactions
D-mannose absorption and efficacy can be influenced by timing relative to meals and other medications. While D-mannose can be taken with or without food, some evidence suggests that administration on an empty stomach may enhance absorption and achieve higher urinary concentrations more rapidly.
Patients should avoid consuming cranberry juice alongside D-mannose, as cranberry juice may alter urinary pH and potentially reduce the supplement's efficacy.
For patients experiencing gastrointestinal side effects, taking D-mannose with food may improve tolerance while maintaining therapeutic efficacy. The timing of doses throughout the day should consider individual lifestyle factors and urination patterns to optimize urinary contact time and therapeutic benefit.
Monitoring and Assessment
Regular monitoring of treatment response involves tracking UTI recurrence rates, symptom severity, and any adverse effects experienced during therapy. Patients should maintain symptom diaries and report any changes in urinary patterns, side effects, or breakthrough infections to healthcare providers.
Laboratory monitoring is generally not required for routine D-mannose therapy, though patients with underlying medical conditions or those taking other medications may benefit from periodic assessment of kidney function and other relevant parameters. Urine cultures may be helpful for confirming UTI diagnosis and guiding treatment decisions in cases of suspected treatment failure.
Safety Profile and Adverse Effects
D-mannose demonstrates an excellent safety profile with minimal reported adverse effects in clinical studies and post-marketing surveillance. The most commonly reported side effects include mild gastrointestinal symptoms such as loose stools, bloating, or nausea, which typically resolve with continued use or dose reduction.
The low incidence of adverse effects relates to D-mannose’s limited systemic absorption and rapid renal elimination, which minimizes accumulation and systemic exposure. Unlike antibiotics, D-mannose does not disrupt normal bacterial flora, reducing the risk of secondary infections or antibiotic-associated complications.
Drug interactions with D-mannose are minimal due to its simple chemical structure and elimination pathway. However, patients taking medications that affect kidney function or glucose metabolism should inform healthcare providers about D-mannose use to ensure appropriate monitoring and dose adjustments if necessary.
Long-term safety data from clinical studies spanning up to two years demonstrate sustained safety with no evidence of cumulative toxicity or organ dysfunction. This safety profile supports the use of D-mannose for long-term prophylactic therapy in patients with recurrent UTIs who require sustained protection.
D-mannose supplements are not a substitute for professional medical care. Individuals, especially those with underlying health conditions, pregnant or breastfeeding women, children, and pet owners, should seek health advice from a qualified medical professional before starting any new supplement or making changes to their health routine. Always consult a medical professional to ensure safe and appropriate use.
Bladder Health and Chronic UTIs
When you're dealing with the heartache of chronic UTIs, those recurring infections that seem to never give you peace, you deserve to know about D-mannose – a truly wonderful natural option that I'm passionate about sharing. This gentle yet powerful supplement, whether you choose tablets or powder, works beautifully by preventing harmful bacteria from clinging to your bladder wall, which is where these troublesome infections love to take hold. I've seen how this natural approach can bring such relief to those who've been caught in that exhausting cycle of repeated infections, offering you the chance to experience fewer flare-ups and much gentler symptoms.
For those of you navigating chronic UTIs, I deeply believe in weaving D-mannose into a loving, comprehensive approach that honors your whole body's needs through thoughtful dietary choices and nurturing lifestyle changes. Simple yet profound shifts – like staying beautifully hydrated, embracing gentle personal hygiene practices, and nourishing yourself with a balanced, wholesome diet – can work hand in hand with D-mannose to support your precious bladder health. I always encourage connecting with a caring healthcare professional, especially if you're expecting or managing other health concerns, because your journey deserves personalized attention and the safest, most appropriate guidance tailored just for you.
Bringing D-mannose into your daily rhythm can be such an empowering step toward taking gentle control of your UTI symptoms, reducing those frustrating infections, and reclaiming the quality of life you deserve. For anyone experiencing recurring UTIs, this natural, well-tolerated option offers hope – a beautiful complement to other healing therapies that can support your long-term bladder wellness and help minimize the burden these chronic infections place on your life.
Integration with Comprehensive UTI Prevention Strategies
D-mannose therapy should be integrated within comprehensive UTI prevention strategies that address multiple risk factors and incorporate evidence-based lifestyle modifications. As D-mannose is considered a food supplement, it should be used as part of a broader plan to prevent urinary tract infections, not as a substitute for a varied diet or healthy lifestyle. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including balanced nutrition and regular physical activity, is essential alongside D-mannose use to support overall wellness and prevention efforts.
Adequate fluid intake, particularly water consumption, supports D-mannose efficacy by maintaining optimal urinary concentrations while promoting regular bladder emptying that helps eliminate bacteria before colonization can occur. Patients should aim for 2-3 liters of fluid daily unless contraindicated by medical conditions.
Hygiene practices including proper wiping techniques, post-coital urination, and appropriate genital hygiene can complement D-mannose therapy by reducing bacterial introduction into the urinary tract. Patient education about these practices enhances overall prevention effectiveness.
Dietary considerations may include reducing refined sugar intake, which can promote bacterial growth, while increasing consumption of foods with natural anti-bacterial properties. Cranberry products, though less effective than D-mannose, may provide complementary benefits when used in combination.

Clinical Evidence and Research Developments
Current clinical evidence supporting D-mannose efficacy continues to expand, with multiple randomized controlled trials demonstrating its effectiveness for UTI prevention and symptom management. A landmark study published in the European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences showed that D-mannose reduced UTI recurrence by 45% compared to placebo while demonstrating non-inferiority to antibiotic prophylaxis. Many of these studies specifically include patients with recurrent cystitis, highlighting the potential benefits for individuals experiencing multiple episodes of urinary tract infections.
Ongoing research investigations are exploring optimal dosing protocols, combination therapies, and expanded applications for D-mannose in urological health. Studies examining D-mannose efficacy in complicated UTIs, catheter-associated infections, and immunocompromised populations may expand therapeutic applications and provide additional clinical guidance. Notably, products such as Waterfall D Mannose Tablets have been evaluated in clinical trials, with customers finding the right dosage and product based on their personal experiences and feedback.
Mechanistic research continues to elucidate the precise mechanisms by which D-mannose prevents bacterial adhesion and whether additional anti-inflammatory or immunomodulatory effects contribute to its therapeutic benefits. Understanding these mechanisms may guide future development of enhanced formulations or combination therapies.
Future directions in D-mannose research include investigation of personalized dosing strategies based on individual bacterial susceptibility patterns, genetic factors affecting metabolism, and biomarker-guided therapy optimization. There is a clear need for future research, particularly larger and well-designed randomized controlled trials, to address current gaps in evidence and to explore combined treatment strategies. These advances may further improve therapeutic outcomes while minimizing treatment failures.
Conclusion and Clinical Recommendations
D-mannose represents a valuable, evidence-based intervention for UTI prevention and management that offers significant advantages over traditional antibiotic prophylaxis including excellent safety profile, minimal adverse effects, and absence of antibiotic resistance concerns. Optimal dosing protocols depend on intended use, with 1-2 grams daily for prevention and 1.5-3 grams 2-3 times daily for active infection management.
Clinical implementation should consider individual patient factors including age, kidney function, concurrent medications, and UTI history when determining appropriate dosing strategies. Regular monitoring and patient education enhance treatment success while minimizing potential adverse effects or treatment failures.
Healthcare providers should consider D-mannose as a first-line option for UTI prevention in appropriate patients, particularly those with recurrent infections, antibiotic allergies, or concerns about antibiotic resistance. Integration with comprehensive prevention strategies maximizes therapeutic benefits while addressing multiple risk factors.
Future clinical practice may benefit from expanded research into personalized dosing approaches, combination therapies, and extended applications for D-mannose in urological health. Continued surveillance of safety and efficacy data will guide optimal utilization of this promising therapeutic intervention for UTI prevention and management.
Many D-mannose products are gluten free, dairy free, nut free, peanut free, soya free, egg free, mustard free, celery free, lupin free, crustacean free, mollusc free, sulphite free, fish free, and sesame free, making them suitable for individuals with various allergies and dietary restrictions. D-mannose supplements should be stored in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight to preserve their quality.
It is essential for patients to consult healthcare professionals and medical professionals before starting D-mannose supplementation to ensure safety and appropriateness based on individual health needs. The growing body of evidence supporting D-mannose efficacy, combined with its excellent safety profile and patient acceptance, positions this natural supplement as an important tool in the prevention and management of urinary tract infections across diverse patient populations seeking safe, effective alternatives to conventional antibiotic approaches.









