The Role of Carnitine in Fitness: Benefits, Risks, and Recommendations
Introduction to Carnitine
- Carnitine is a conditionally essential amino acid derivative involved in fatty acid metabolism and energy production.
- It plays a crucial role in transporting fatty acids into mitochondria to produce adenosine triphosphate (ATD), which is vital for energy production in skeletal muscle and heart.
- Carnitine is naturally found in animal foods and can also be synthesized in the liver, kidneys, and brain.
- Dietary carnitine is abundant in red meat, poultry, and fish, with limited availability in plant-based foods. Its bioavailability is crucial for energy production and fatty acid transport, making it an essential component of a healthy diet.

Mechanism of Action
L-carnitine plays a pivotal role in the transportation of fatty acids into the mitochondria, the powerhouse of the cell, where they are converted into energy. This process is crucial for the production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the primary energy source for the body. By facilitating the entry of fatty acids into the mitochondria, L-carnitine ensures that these molecules are efficiently utilized for energy production, particularly in skeletal muscle and the heart.
Moreover, L-carnitine helps to remove excess fatty acids from the mitochondria, preventing potential damage to the cells. This dual role not only supports energy production but also protects cellular integrity. Additionally, L-carnitine exhibits antioxidant properties, which help to shield cells from oxidative stress and damage. In the context of amino acid supplements, L-carnitine is considered a conditionally essential nutrient. While the body can synthesize it, certain conditions such as high-energy demands or specific health conditions may necessitate supplementation to meet the body’s needs.
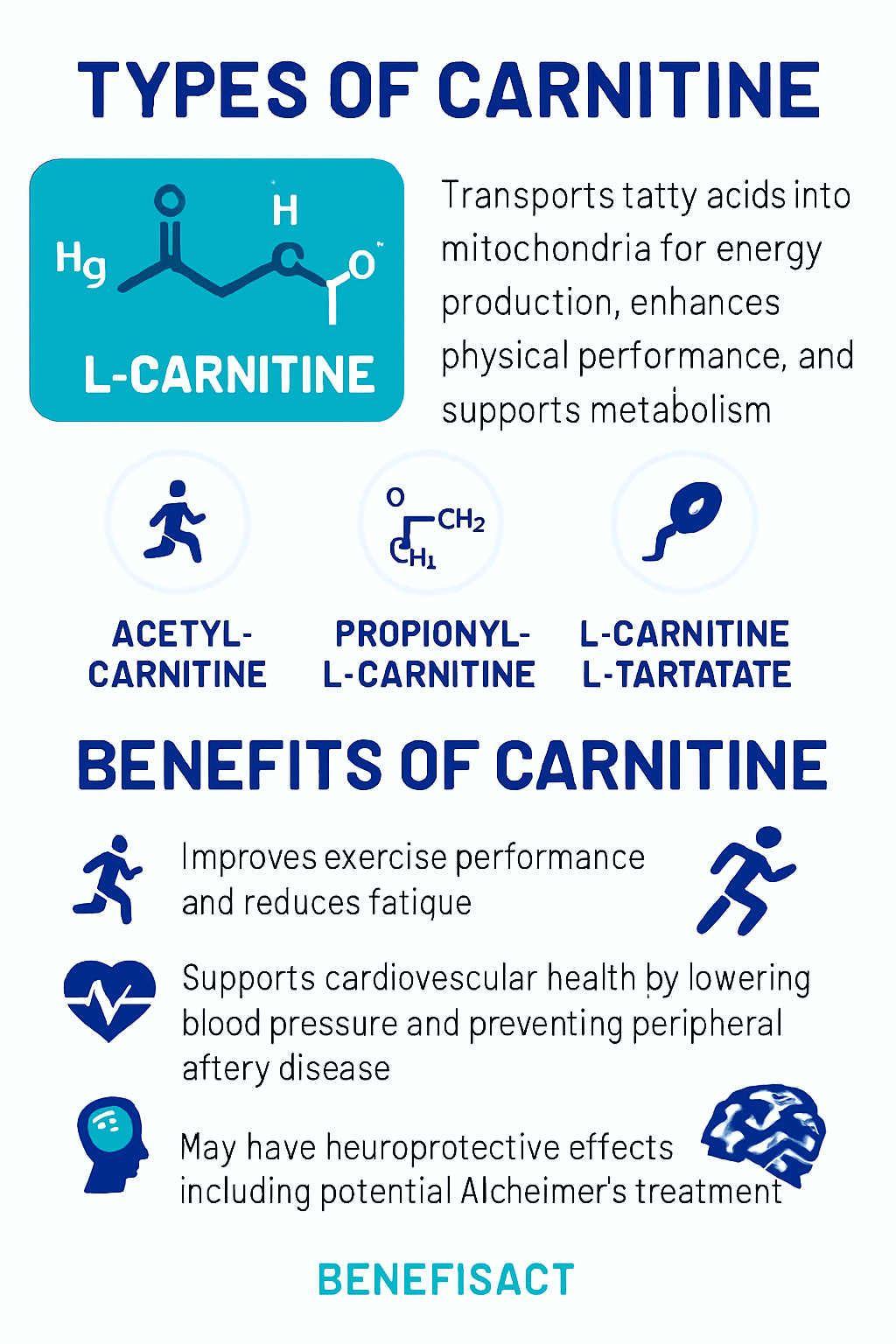
Types of Carnitine
Carnitine exists in several forms, each with unique functions and benefits. The most commonly used form is L-carnitine, which is integral to the transportation of fatty acids into the mitochondria for energy production. This form is widely recognized for its role in enhancing physical performance and supporting metabolic processes.
Acetyl-L-carnitine, another prominent form, is particularly beneficial for brain health. It crosses the blood-brain barrier and is involved in the production of energy within brain cells. Studies have shown that acetyl-L-carnitine has neuroprotective effects, making it a potential supplement for cognitive health and neurodegenerative conditions.
Propionyl-L-carnitine is primarily associated with cardiovascular health. It aids in the production of energy in heart cells and has been shown to improve blood flow and reduce symptoms of peripheral artery disease. These amino acid derivatives, including various forms of carnitine, play crucial roles in energy production, metabolism, and overall health.

Benefits of Carnitine
- Carnitine supplementation, including oral l-carnitine supplementation, has been shown to improve exercise performance and reduce fatigue in healthy athletes.
- It may also have benefits for cardiovascular health, including lowering blood pressure and preventing peripheral artery disease.
- Carnitine has been found to improve sperm motility and sperm quality parameters, making it a potential supplement for individuals with erectile dysfunction.
- Additionally, carnitine may have neuroprotective effects and has been studied as a potential treatment for Alzheimer’s disease.
Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosage of L-carnitine can vary based on individual needs and health status. For most people, a daily dosage of 500-2000 mg is considered safe and effective. However, specific health goals or conditions may require higher dosages. For instance, some studies have used dosages of up to 3000-4000 mg per day to achieve benefits such as enhanced exercise performance or improved cardiovascular health.
It is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before starting L-carnitine supplementation, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking medications. Amino acid supplements, including L-carnitine, can interact with various medications, such as blood thinners, diabetes medications, and treatments for high blood pressure. Personalized medical advice ensures that supplementation is both safe and effective.

Risks and Carnitine Deficiency
- Carnitine deficiency can occur due to genetic disorders, certain medications, or underlying renal diseases, leading to detrimental effects on kidney function and energy production.
- A carnitine deficiency can cause significant adverse effects, including fatigue, weakness, and heart problems.
- Individuals with end-stage renal disease or those taking certain medications may be at risk of carnitine deficiency.
- It is essential to monitor serum creatinine levels and kidney function when taking carnitine supplements, especially for individuals with pre-existing kidney disease, as serum creatinine level elevation can indicate worsening renal function.
Dietary L Carnitine Sources and Supplements
- Dietary sources of carnitine include red meat, dairy products, fish, and whole grains, which are rich in amino acids and other essential nutrients.
- Carnitine supplements are available in various forms, including l-carnitine and acetyl-l-carnitine, which can be used to support energy production and fatty acid metabolism.
- When taking amino acid supplements, including carnitine, it is crucial to follow the recommended optimal daily dose and intake duration to minimize potential adverse effects.
- Additionally, individuals should be aware of the potential interactions between carnitine and other supplements, such as creatine supplementation and glutamine supplementation.
- It is important to evaluate the risks and benefits of common supplemental amino acids, including L-carnitine, L-arginine, and glutamine, particularly concerning kidney function. Understanding the renal safety and potential adverse effects can help determine optimal dosages that minimize renal adverse effects in athletes and bodybuilders.
Interactions with Other Supplements and Oral L Carnitine Supplementation
- Carnitine may interact with other supplements, including vitamin C, and certain medications, such as blood thinners.
- It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before taking carnitine supplements, especially when combined with other amino acid supplements like l-arginine. When taking l arginine, it is particularly important to seek medical advice to ensure safety and proper dosage.
- Individuals with underlying health conditions, such as high blood pressure or kidney disease, should exercise caution when taking carnitine supplements.
- Moreover, carnitine may have synergistic effects when combined with other supplements, such as creatine and glutamine, which can enhance athletic performance and muscle growth.
Scientific Studies and Evidence
Numerous scientific studies have explored the effects of L-carnitine supplementation on various health outcomes. Research has consistently shown that L-carnitine can enhance exercise performance, reduce fatigue, and support cardiovascular health. For example, athletes taking L-carnitine have reported improved endurance and reduced muscle soreness.
Additionally, L-carnitine has demonstrated neuroprotective effects, making it a potential supplement for individuals with neurodegenerative conditions like Alzheimer’s disease. However, while the existing data is promising, more research is needed to fully understand the optimal dosage, duration of treatment, and long-term effects of L-carnitine supplementation.
The renal safety of L-carnitine, along with other amino acid supplements like L-arginine and glutamine, has been evaluated in several studies. These studies indicate that while these supplements can offer benefits, they may also have detrimental effects on kidney function in certain individuals. Therefore, it is essential to monitor kidney health and consult healthcare professionals when considering these supplements.
Targeted Benefits for Specific Populations
L-carnitine supplementation can offer targeted benefits for specific populations, particularly athletes and individuals with cardiovascular disease. Athletes may find L-carnitine beneficial for improving exercise performance and reducing fatigue, allowing for more intense and prolonged training sessions.
For individuals with cardiovascular disease, L-carnitine can support heart health by improving blood flow and reducing the risk of heart disease. Additionally, L-carnitine has shown promise in improving erectile dysfunction by enhancing blood flow and reducing inflammation, which can positively impact sperm quality parameters.
Amino acid supplements, including L-carnitine, can support overall health and wellness, especially in individuals with underlying health conditions or those at risk of developing certain health issues. However, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any supplementation regimen to ensure safety and efficacy, particularly if you have existing health conditions or are taking medications.
Health Benefits and Risks
- The health benefits of carnitine supplementation include improved exercise performance, cardiovascular health, and potential neuroprotective effects.
- However, potential risks and adverse effects include gastrointestinal side effects, interactions with medications, and exacerbation of underlying health conditions.
- More clinical data and research are needed to fully understand the benefits and risks of carnitine supplementation, particularly in individuals with underlying renal diseases or kidney injury. A comprehensive evaluation of the available data is crucial to understand these potential risks and benefits.
- Additionally, the effects of carnitine on kidney function and renal safety should be carefully evaluated, especially in individuals with pre-existing kidney disease or those taking certain medications.
Conclusion and Recommendations
- In conclusion, carnitine is a conditionally essential amino acid derivative that plays a crucial role in energy production and fatty acid metabolism.
- Healthy adults and athletes may benefit from carnitine supplementation, but it is essential to follow the recommended optimal daily dose and intake duration.
- Individuals with underlying health conditions or taking certain medications should consult with a healthcare professional before taking carnitine supplements.
- Further research is needed to fully understand the benefits and risks of carnitine supplementation, and individuals should be aware of the potential interactions with other supplements and medications to ensure safe and effective use.