The human body comes equipped with a remarkably sophisticated detoxification system. The liver, kidneys, skin, and lungs work around the clock to process and eliminate waste products, environmental toxins, and metabolic byproducts. While no supplement can replace these built-in systems, certain vitamins play critical roles in supporting and optimising these natural pathways.
Understanding which vitamins directly contribute to detoxification processes allows individuals to make informed decisions about their nutritional intake. This guide examines four key vitamins that scientific research has linked to enhanced detoxification support: without the hype or exaggerated claims often found in wellness marketing.
How the Body's Detoxification System Works
Before diving into specific vitamins, it helps to understand what "detoxification" actually means from a biological standpoint.
The liver performs detoxification in two primary phases:
- Phase I (Activation): Enzymes, particularly the cytochrome P450 family, convert fat-soluble toxins into intermediate compounds. This process requires specific nutrients to function properly.
- Phase II (Conjugation): The liver attaches molecules to these intermediates, making them water-soluble and safe for elimination through urine or bile.
The kidneys then filter blood, removing these water-soluble waste products for excretion. Both systems require adequate nutritional support to operate efficiently.
1. Vitamin C: The Antioxidant Powerhouse
Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) serves multiple functions in detoxification pathways. Its primary role involves neutralising free radicals generated during Phase I liver detoxification: a process that paradoxically creates oxidative stress as a byproduct.
Key Functions in Detoxification:
- Glutathione Regeneration: Vitamin C helps recycle glutathione, often called the body's "master antioxidant." Glutathione directly binds to toxins during Phase II detoxification, making its availability crucial for efficient toxin processing.
- Collagen Synthesis: Beyond detox, vitamin C supports the structural integrity of organs involved in elimination, including the gut lining and blood vessels.
- Heavy Metal Chelation: Research indicates vitamin C may assist in binding certain heavy metals, facilitating their removal from the body.
Recommended Approach:
Adults should aim for at least 75-90mg daily, though those seeking enhanced antioxidant support often benefit from higher intakes up to 1,000mg. Food sources include citrus fruits, bell peppers, strawberries, and broccoli. Supplementation offers a convenient alternative when dietary intake falls short.
Important Note: Vitamin C works synergistically with N-acetyl cysteine (NAC), a glutathione precursor. Combining these nutrients may enhance overall antioxidant capacity.
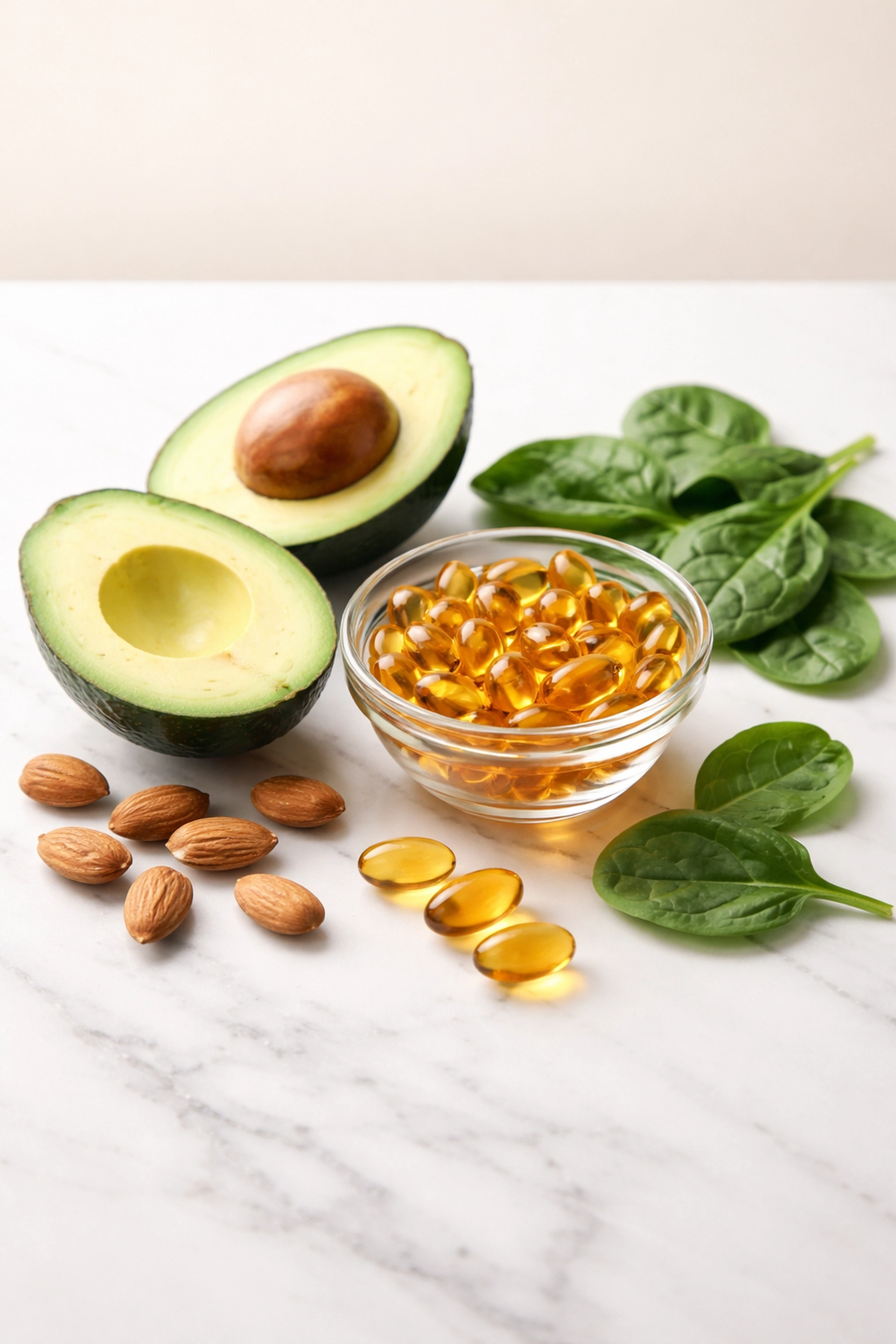
2. Vitamin E: Cell Membrane Protection
Vitamin E exists as a family of eight compounds, with alpha-tocopherol being the most biologically active form in humans. Its fat-soluble nature allows it to embed within cell membranes, providing protection exactly where oxidative damage frequently occurs.
Key Functions in Detoxification:
- Lipid Peroxidation Prevention: During detoxification, free radicals can damage cell membranes through a chain reaction called lipid peroxidation. Vitamin E interrupts this process, protecting cellular integrity.
- Liver Cell Protection: Hepatocytes (liver cells) face constant oxidative stress during toxin processing. Vitamin E helps maintain their structural health and function.
- Synergy with Vitamin C: After neutralising a free radical, vitamin E becomes oxidised. Vitamin C can regenerate vitamin E, allowing it to continue its protective functions.

Recommended Approach:
The recommended daily allowance sits at 15mg (22.4 IU) for adults. Natural food sources include nuts, seeds, spinach, and avocados. When selecting supplements, look for natural vitamin E (d-alpha-tocopherol) rather than synthetic versions (dl-alpha-tocopherol) for better bioavailability.
3. B-Complex Vitamins: The Detox Engine
B vitamins function as essential cofactors: molecules that enzymes require to perform their chemical reactions. Without adequate B vitamin status, both Phase I and Phase II liver detoxification slow significantly.
Individual B Vitamin Roles:
| Vitamin | Detoxification Function |
|---|---|
| B1 (Thiamine) | Supports energy production in liver cells |
| B2 (Riboflavin) | Required for glutathione recycling |
| B3 (Niacin) | Supports Phase I enzyme activity |
| B5 (Pantothenic Acid) | Essential for coenzyme A production |
| B6 (Pyridoxine) | Critical for amino acid metabolism and Phase II conjugation |
| B9 (Folate) | Supports methylation and DNA repair |
| B12 (Cobalamin) | Essential for methylation detox pathways |
Why B Vitamins Work Best Together:
B vitamins operate as a team. A deficiency in one often impairs the function of others. For example, B12 and folate work together in methylation pathways: supplementing one without the other can create imbalances.
Recommended Approach:
Rather than supplementing individual B vitamins, most individuals benefit from a comprehensive B-complex formula. This ensures balanced intake across all eight essential B vitamins. Those following plant-based diets should pay particular attention to B12, as it occurs naturally only in animal products.
For more information on supporting overall health through targeted supplementation, explore our guide on supplements for women over 40.
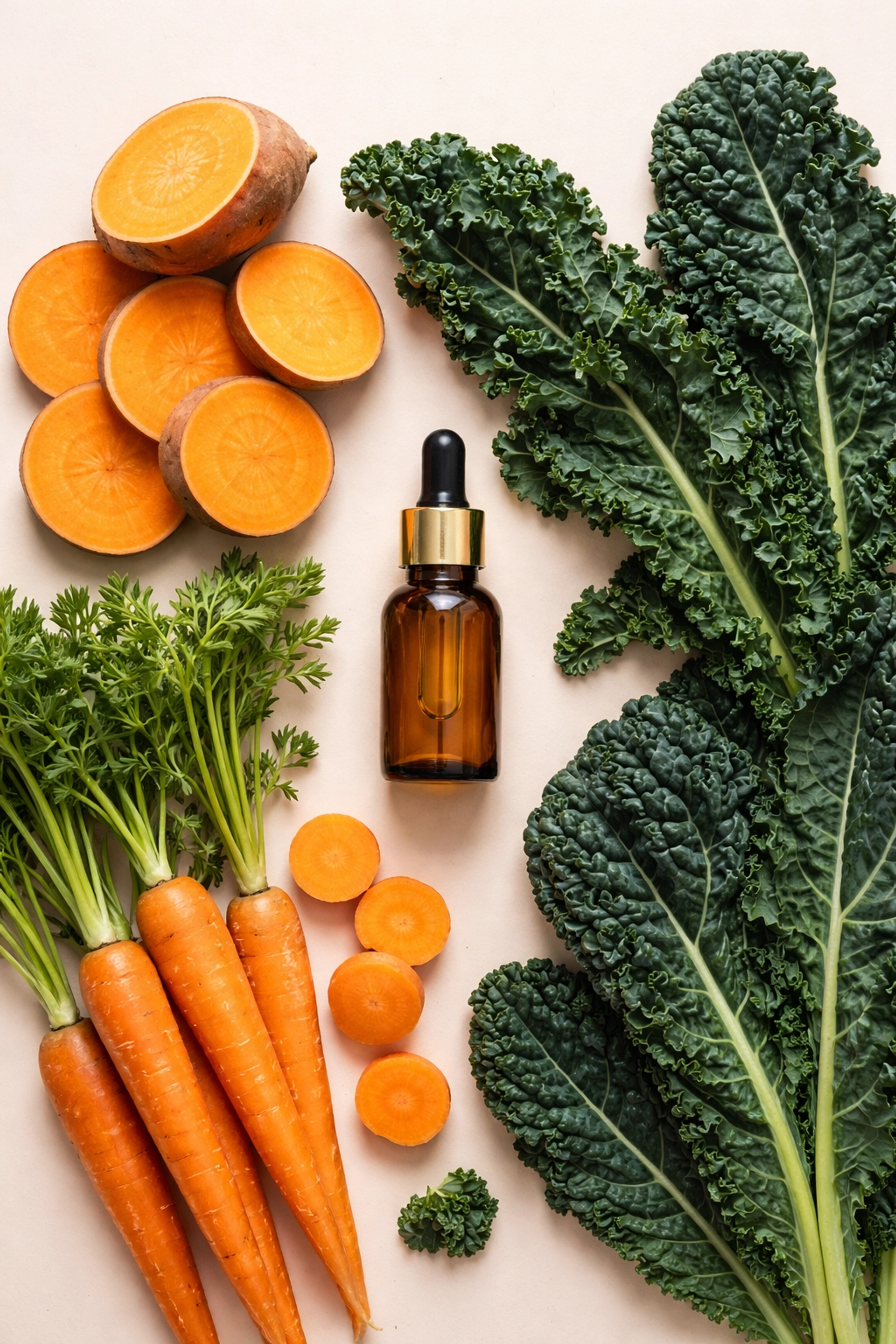
4. Vitamin A: Barrier Defence and Antioxidant Support
Vitamin A often gets overlooked in detoxification discussions, yet it plays two distinct roles in supporting the body's cleansing processes.

Key Functions in Detoxification:
- Mucosal Barrier Integrity: The gut lining serves as the first line of defence against ingested toxins. Vitamin A maintains the health and tight junctions of epithelial cells throughout the digestive tract, preventing unwanted substances from entering the bloodstream.
- Antioxidant Activity: Beta-carotene (provitamin A) functions as an antioxidant, neutralising free radicals before they can cause cellular damage.
- Immune Function: The immune system identifies and neutralises many potential toxins. Vitamin A supports immune cell production and function.
Recommended Approach:
The recommended daily allowance is 700-900mcg RAE (retinol activity equivalents) for adults. Preformed vitamin A (retinol) comes from animal sources like liver, eggs, and dairy. Plant sources provide beta-carotene, which the body converts to vitamin A as needed: find it in orange and dark green vegetables like sweet potatoes, carrots, and kale.
Caution: Unlike water-soluble vitamins, vitamin A accumulates in the body. Excessive supplementation of preformed vitamin A can cause toxicity. Stick to recommended doses and consider beta-carotene sources for a safer approach.
Practical Implementation Guidelines
Supporting the body's detoxification pathways requires more than just vitamin supplementation. Consider these evidence-based strategies:
-
Prioritise whole foods first. Vitamins from food sources come packaged with complementary nutrients, fibre, and phytochemicals that enhance absorption and effectiveness.
-
Stay adequately hydrated. The kidneys require sufficient water to flush water-soluble waste products efficiently. Aim for 2-3 litres daily.
-
Support with quality supplements when needed. Dietary gaps, increased demands, or specific health goals may warrant supplementation.
-
Maintain consistent intake. Detoxification pathways operate continuously. Sporadic high-dose supplementation proves less effective than consistent daily intake.
-
Combine with lifestyle factors. Quality sleep, regular exercise, and stress management all influence detoxification efficiency.
Choosing Quality Supplements
Not all supplements deliver equal results. When selecting vitamin supplements for detoxification support, consider:
- Bioavailable forms: Look for vitamins in their active, readily-usable forms
- Third-party testing: Quality manufacturers verify potency and purity
- Appropriate dosing: More isn't always better: stick to evidence-based amounts
- Sustainable packaging: Environmental responsibility matters
At Fitness Health, all supplements are UK-made under strict quality standards and packaged in eco-conscious paper materials. This commitment ensures both product integrity and environmental responsibility.
The Bottom Line
The body's detoxification systems work remarkably well when properly supported. Vitamins C, E, B-complex, and A each contribute specific functions to these pathways: from antioxidant protection to enzyme cofactor activity to barrier maintenance.
Rather than seeking quick-fix "cleanses," focus on consistent nutritional support through diet and targeted supplementation. This approach works with the body's existing systems rather than promising unrealistic shortcuts.
For those interested in optimising their nutritional foundation, combining these detox-supportive vitamins with adequate protein intake creates a solid baseline for overall health. Check out our high-protein breakfast ideas to start the day with proper nutritional support.














































































